Interactive Models
Patterns in Earth's Surface Temperature
Overview
Using interactive maps of surface (skin) temperature and land cover classification in Austin, Texas, students will analyze how surface (skin) temperatures vary across a community and determine what factors contribute to this variation. Upon completion of this lesson, students will be able to describe how human activity alters the local environment.
This interactive model is one of a three-part sequence of learning experiences related to the Creation of Urban Heat Islands. To maximize optimal learning outcomes, it is suggested to complete the series in the following order:
- Human Impact and the Creation of Urban Heat Islands Interactive Model
- Patterns in Earth's Surface Temperature Interactive Model (current page)
- Exploring the Tradeoffs of Surface Temperature Models
This story map is intended to be used with students who have access to a computing device in a 1:1 or 1:2 setting.
Materials Required
Resources Needed Per Student:
- Student Data Sheet (Optional)
- Computer/Tablet
- Internet Access
- Link to Patterns in Earth's Surface Temperature Interactive Model
Directions
- Using an internet accessible device, students open the link to the Patterns in Earth's Surface Temperature Interactive Model to begin their exploration of this phenomenon.
- Distribute the Patterns in Earth's Surface Temperature Interactive Model Student Sheet (optional). Have students navigate on their own through the interactive model to answer the questions and complete the activities on their student sheet.
Teacher Note
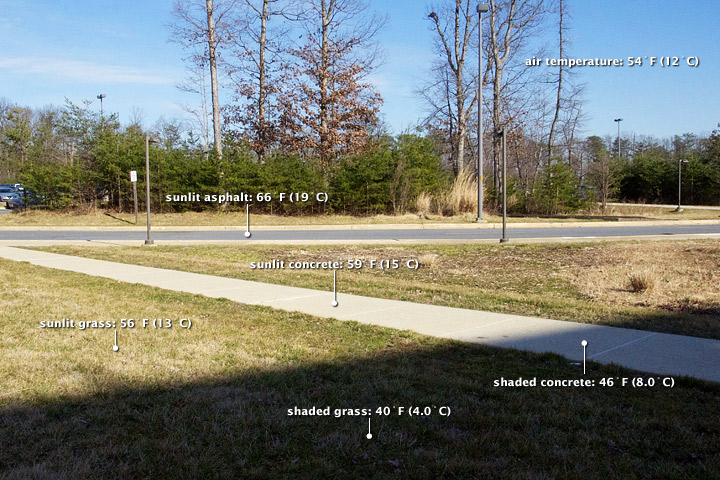
Heat islands form as vegetation is replaced by asphalt and concrete for roads, buildings, and other structures necessary to accommodate growing populations. These surfaces absorb—rather than reflect— the sun's heat, causing surface temperatures and near-surface air temperatures to rise near these surfaces. Displacing trees and vegetation minimizes the natural cooling effects of shading and evaporation of water from soil and leaves (evapotranspiration).
To learn more, visit:
- The Urban Heat Island Phenomena page for background information.
Teachers who are interested in receiving the answer key, please complete the Teacher Key Request and Verification Form. We verify that requestors are teachers prior to sending access to the answer keys as we’ve had many students try to pass as teachers to gain access.
Disciplinary Core Ideas:
- ESS2A: Earth Materials and Systems
- ESS3C: Human Impacts on Earth Systems
Crosscutting Concepts:
- Patterns
Science and Engineering Practices:
- Developing and Using Models
- Analyzing and Interpreting Data
- Students will analyze how surface (skin) temperatures vary among a community and determine what factors contribute to this variation.
- Students will describe the relationship between surface (skin) temperature and surface air temperature.
- How does human activity affect the local environment?
- What factors contribute to variation in surface (skin) temperatures across a community?
- What factors affect air temperature in a community?
- Internet Required