The Earth's system is characterized by the interaction of processes that take place on molecular (very small) and planetary (very large) spatial scales, as well as on short and long time scales. Before scientists may begin their work with these data, it is important that they understand what the data are.
>> Read More >>
Just one moment,
loading Earth as a System...
Featured Mini Lessons
-
-
-
-
-
Grade Level: 6-8
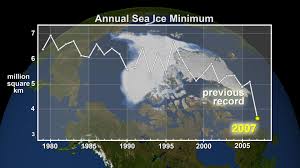
Arctic sea ice is the cap of frozen seawater blanketing most of the Arctic Ocean and neighboring seas in wintertime. It follows seasonal patterns of thickening and melting. Students view how the quantity has changed from 1979 through 2018.
Grade Level: 6-8, 9-12
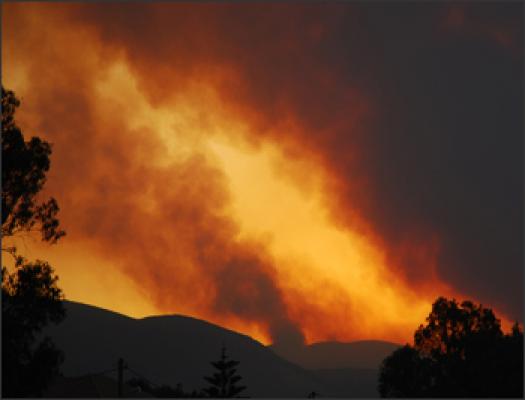
The fires in Greece during the summer of 2007 devastated large tracks of forest and ground cover in this Mediterranean region. Students analyze these data to determine the scale, area, and percentage of the forest impacted by of these fires.
Grade Level: 6-8, 9-12
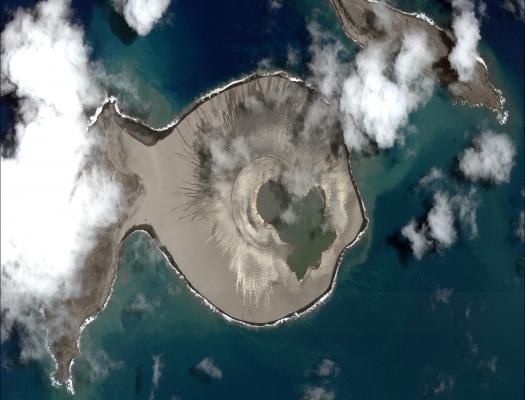
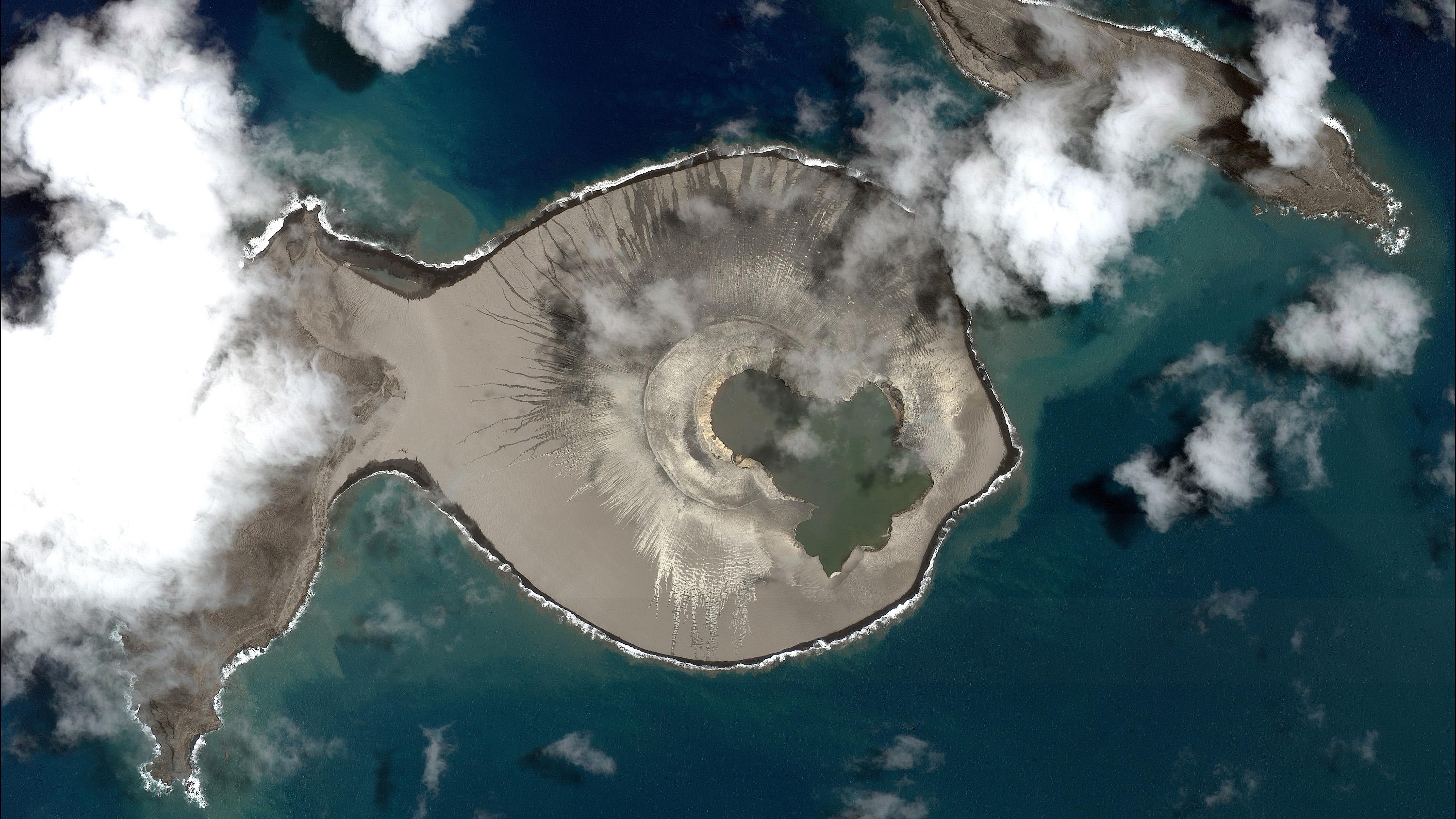
Students will describe the changes in a newly-formed volcanic island over the first three years of its life.
Grade Level: 6-8, 9-12
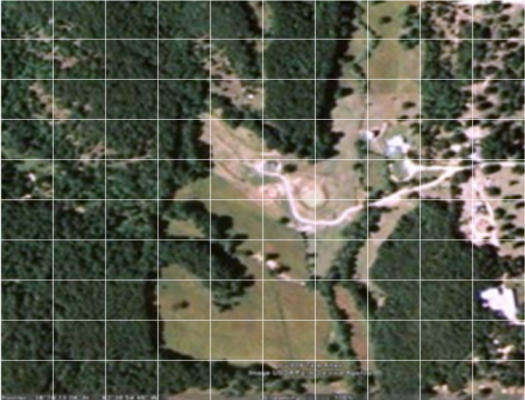
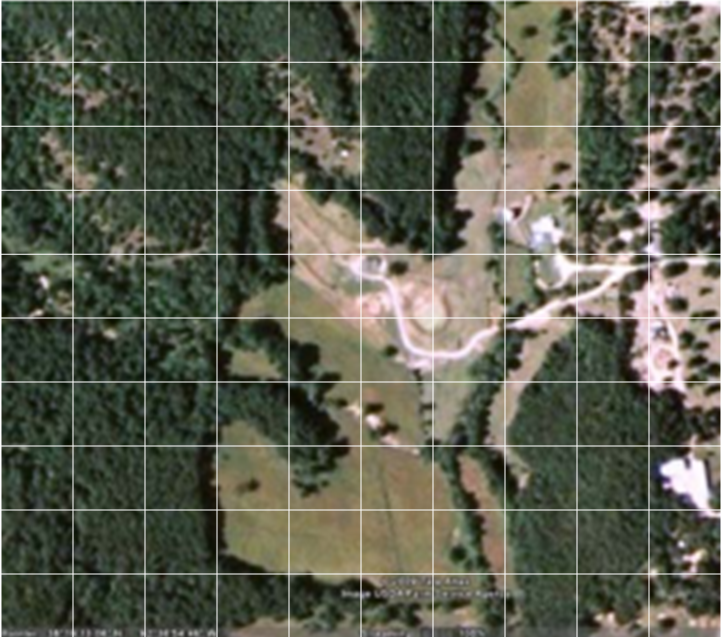
Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is affected by many processes including fires, deforestation, and plant respiration. Students will evaluate a Landsat image to determine the rate of carbon dioxide sequestration in a particular area.
Grade Level: 6-8, 9-12
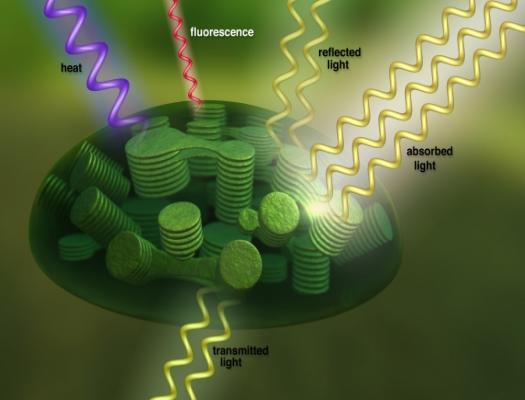
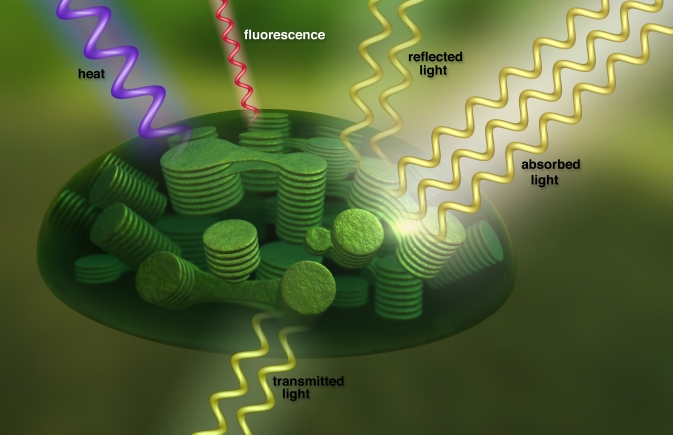
Students learn how to estimate the "energy efficiency" of photosynthesis, or the amount of energy that plants absorb for any given location on Earth.
Previous
Next
Grade Level: 6-8
Arctic sea ice is the cap of frozen seawater blanketing most of the Arctic Ocean and neighboring seas in wintertime. It follows seasonal patterns of thickening and melting. Students view how the quantity has changed from 1979 through 2018.
Grade Level: 6-8,
9-12
The fires in Greece during the summer of 2007 devastated large tracks of forest and ground cover in this Mediterranean region. Students analyze these data to determine the scale, area, and percentage of the forest impacted by of these fires.
Grade Level: 6-8,
9-12
Students will describe the changes in a newly-formed volcanic island over the first three years of its life.
Grade Level: 6-8,
9-12
Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is affected by many processes including fires, deforestation, and plant respiration. Students will evaluate a Landsat image to determine the rate of carbon dioxide sequestration in a particular area.
Grade Level: 6-8,
9-12
Students learn how to estimate the "energy efficiency" of photosynthesis, or the amount of energy that plants absorb for any given location on Earth.
Scale, Proportion, and Quantity landing page. Explore maps, graphs, data, and related education resources. These resources include lesson plans, mini lessons, activities, and datasets for teachers and students.