Solar Eclipses

Remember to never look directly at the Sun without proper safety equipment.
What is a solar eclipse?
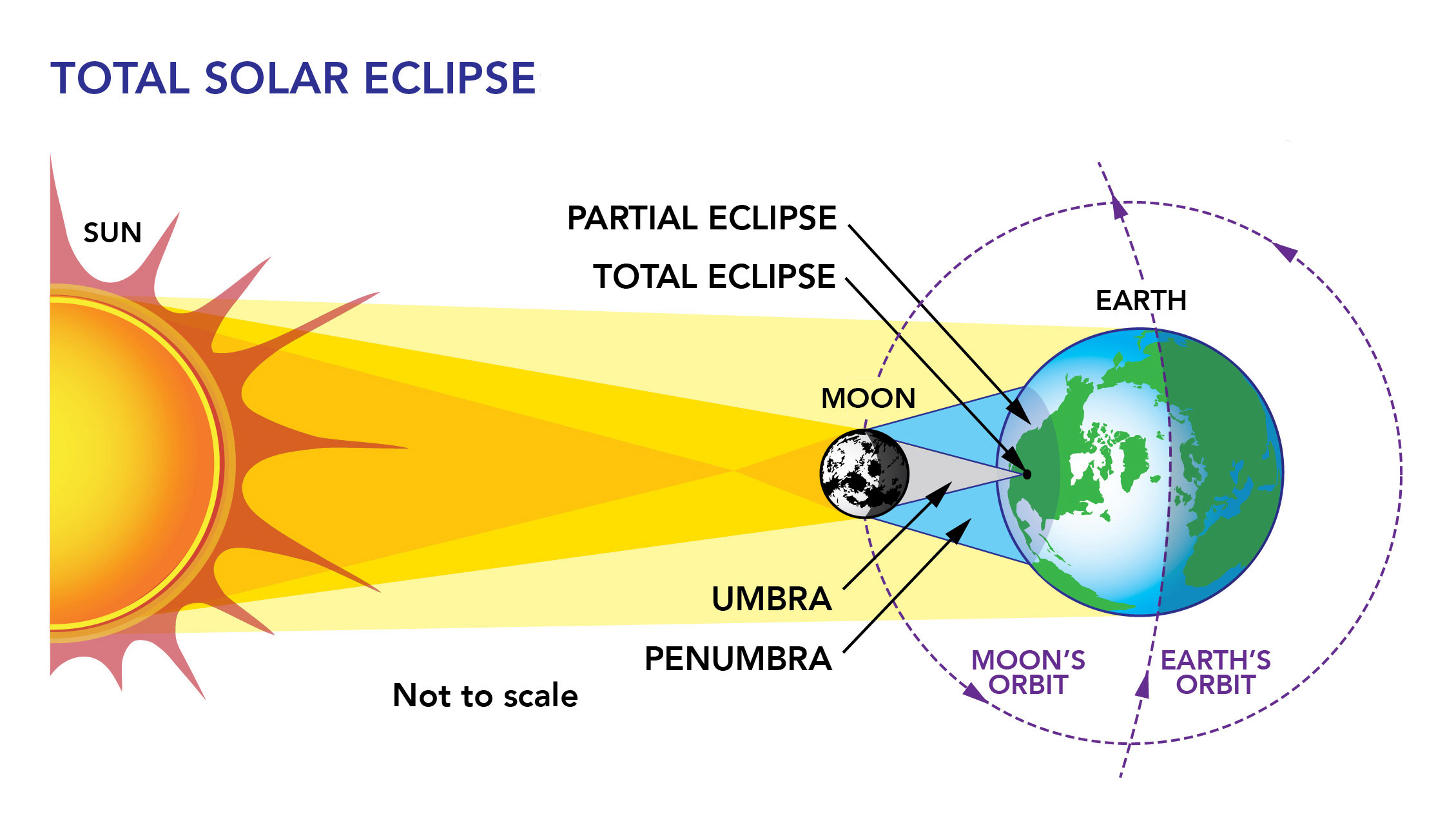
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon is between the Sun and Earth, and with the right conditions, the Moon casts a shadow on Earth’s surface.

The phenomenon of a solar eclipse is possible because even though the Sun is about 400 times larger than the Moon, the Sun is about 400 times farther away from Earth than the Moon is. This ratio of the size and distance of these objects makes them appear the same size in the sky.
What are the different types of solar eclipses?
A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely blocks the Sun; a partial solar eclipse occurs when only part of the Sun is blocked by the Moon. A third type of solar eclipse happens when the Moon is farther away in its orbit around the Earth and appears smaller, only blocking 90% of the Sun’s disk. Although technically a partial solar eclipse, this type of eclipse is called an annular solar eclipse.

Total vs. Partial Solar Eclipses
The difference between a total and partial eclipse is where in the Moon’s shadow the observer is located. Observers in the umbra shadow will experience a total solar eclipse. Observers in the penumbra shadow will experience a partial solar eclipse. The umbra shadow is much smaller, making experiencing a total solar eclipse more rare.

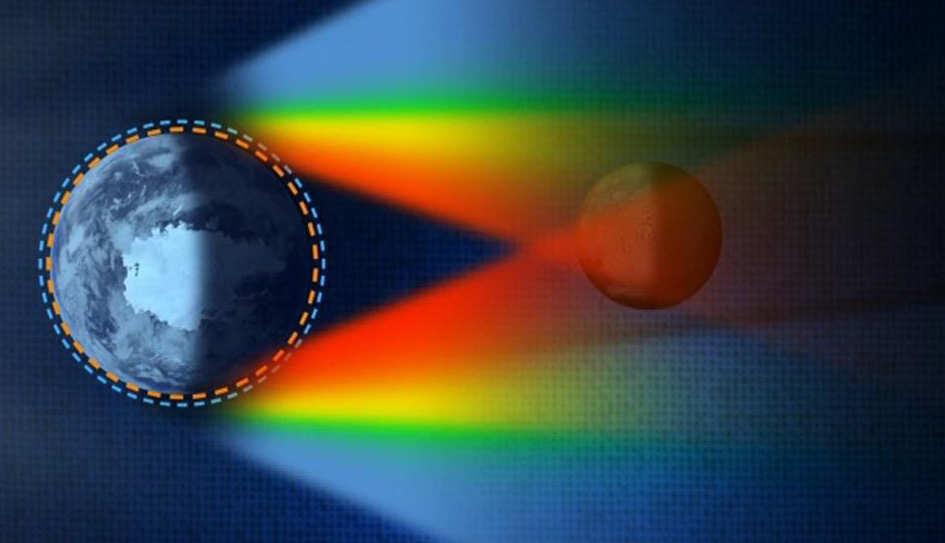
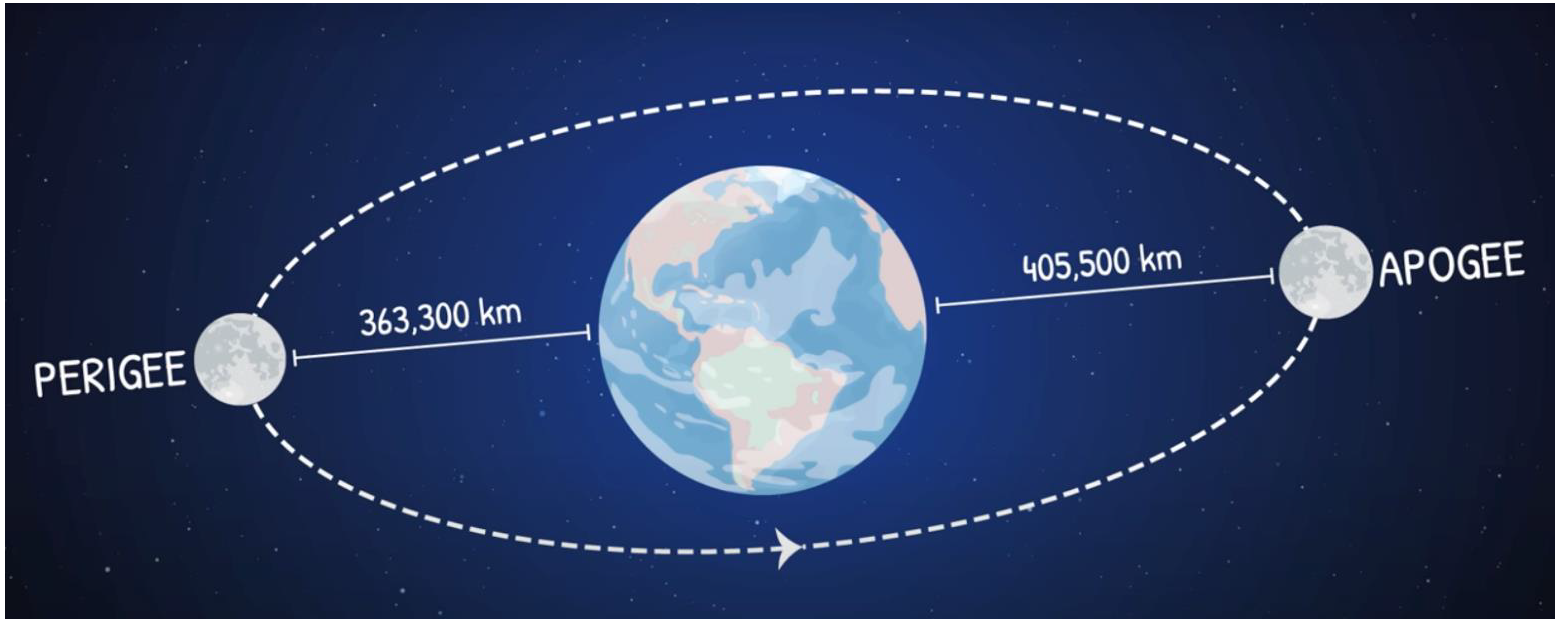
Total vs. Annular Solar Eclipses
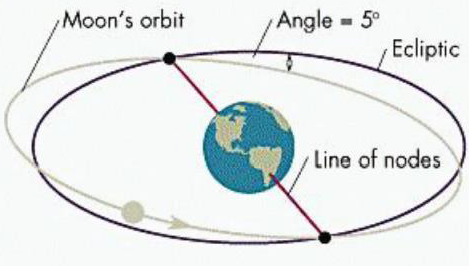
The difference between a total and annular eclipse is the distance between the Moon and Earth. The reason that the Moon is not always the same distance from Earth is because the shape of the Moon’s orbit around Earth is in the shape of an ellipse, or an oval. During a solar eclipse, if the Moon is closer to perigee, the eclipse will be total. If the Moon is closer to apogee, the eclipse will be annular.
Solar Eclipse Safety
Always use the proper safety equipment to observe the Sun. Solar filters are 1000 times darker than sunglasses and block all infrared and UV light, and nearly all visible light. If you don’t have solar eclipse glasses or a solar filter for your telescope or binoculars, there are indirect ways to safely observe the Sun, like using a pinhole projector.

Solar eclipses can help understand how the Sun impacts Earth Systems
Observing solar eclipses helps scientists learn more about how the Sun creates space weather. Space weather is caused by the solar wind, which originates from the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona. Space weather occurs when the solar wind intensifies and can impact systems on Earth. The corona is usually hidden by the bright light of the Sun's surface, which makes it difficult to see without using special instruments. However, the corona can be viewed with the naked eye only during totality of a total solar eclipse.
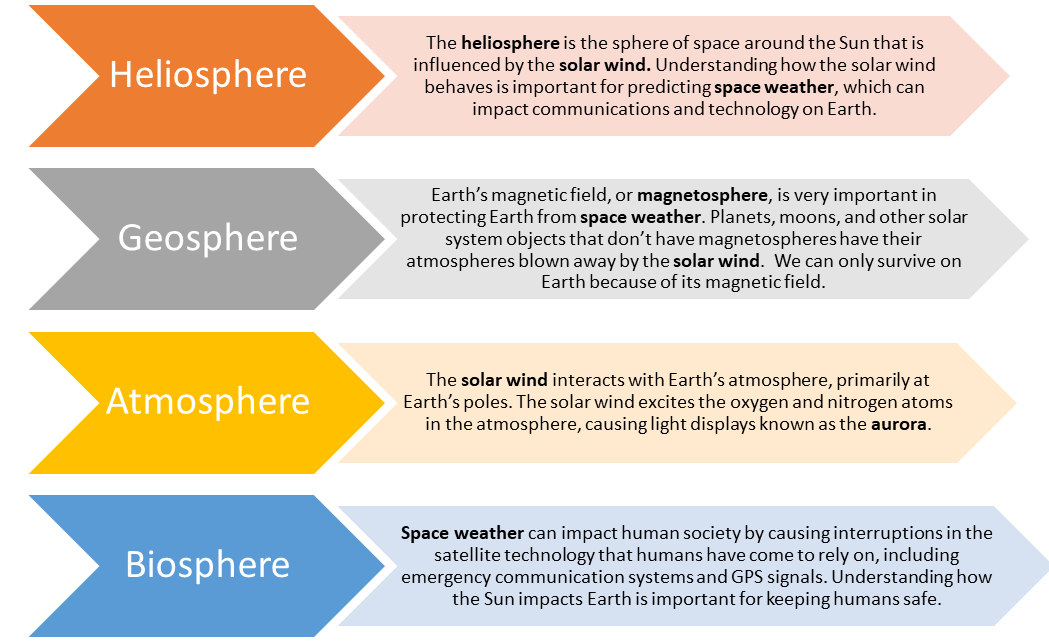
Space weather from the Sun's heliosphere interacts with Earth's geosphere, atmosphere and biosphere., Credit: NASA, https://mynasadata.larc.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/inline-images/MND%20Graphic%20for%20System%20Science.png
This product is supported by the NASA Heliophysics Education Activation Team (NASA HEAT), part of NASA's Science Activation portfolio.
Sources
- Types | About. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. Retrieved February 5, 2023, from https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/eclipses/about-eclipses/types/
- Types | About. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. Retrieved March 2, 2023, from https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/eclipses/about-eclipses/types
- Supermoons | Moon in Motion – Moon: NASA Science. (2021, May 26). Moon. Retrieved February 26, 2023, from https://moon.nasa.gov/moon-in-motion/supermoons/
- Geometry | Science – NASA Solar System Exploration. (n.d.). NASA Solar System Exploration. Retrieved April 6, 2023, from https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/eclipses/science/geometry/