Data scientists work with data captured by scientific instruments or generated by a simulator, as well as data that is processed by software and stored in computer systems. They work with scientists to analyze databases and files using data management techniques and statistics.
A Data Support Specialist works with the user community to understand their science needs with the goal of providing support for NASA data and information services. They represent the user in product development and development resources to assist with the user community's needs.
Mathematical modelers use mathematics to create models that demonstrate complex processes or solve problems. Many mathematical modelers use their skills to create and animate 3D representations of their processes with the assistance of software technology.
A model analyst develops models to help visualize, observe, and predict complicated data. Model analysis is the process of taking large amounts of data and separate it into a structure that makes it intelligible to the binary process of computers.
At the core of scientific visualization is the representation of data graphically - through images, animations, and videos - to improve understanding and develop insight.
Follow along as NASA visualizer Kel Elkins walks you through three visualizations (Dust Crossing, Typhoon Hagupit, and Aquarius Sea Surface Salinity) and answers questions about his work, education, and career.
Dr. Dalia B. Kirschbaum is a Research Physical Scientist in the Hydrological Sciences Lab at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD. Learn how she uses mathematics to investigate the interaction between the Hydrosphere & Geosphere.
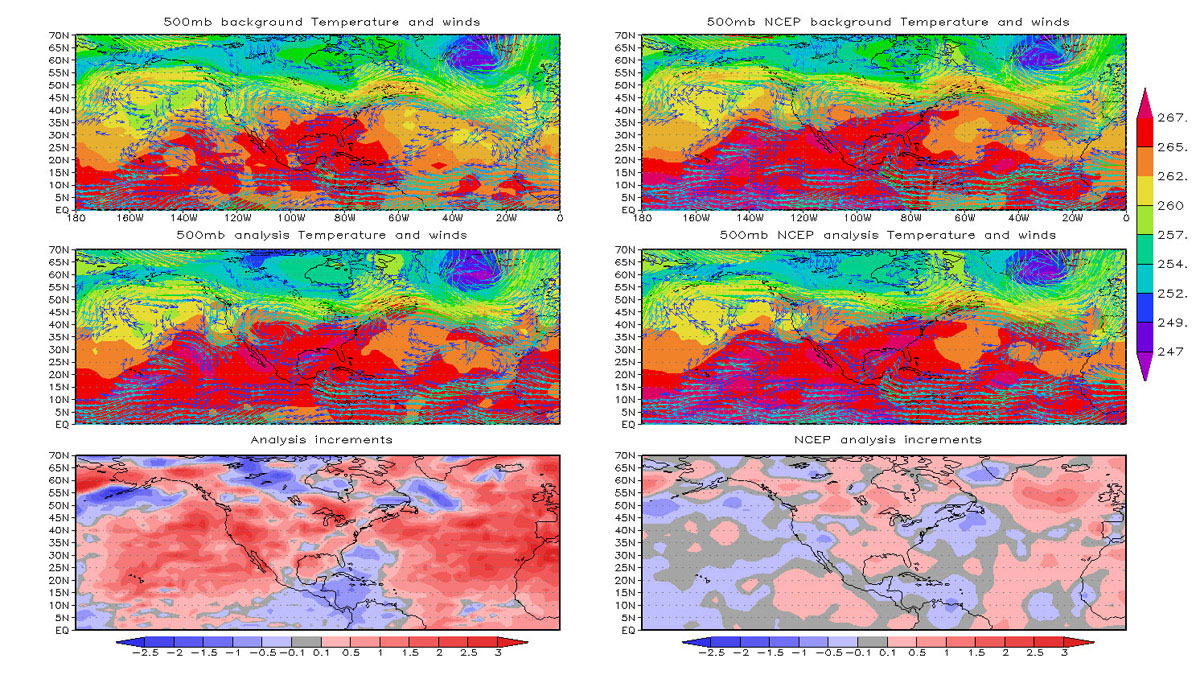
Every day, scientists at NASA work on creating better hurricanes on a computer screen. At NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, a team of scientists spends its days incorporating millions of atmospheric observations.
Ryan Turner says "My career has focused on software and software is ubiquitous, so I have been involved in many different projects. There is a lot of flexibility with software.






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)